Imagine a world where data security and transparency are no longer concerns, where transactions are instant, and users truly own their digital identities. Blockchain, once synonymous only with cryptocurrencies, is now redefining this vision for industries worldwide.
Blockchain, initially recognized through Bitcoin, is now reshaping industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management by securing and decentralizing data. This blog will guide you through blockchain essentials, debunk myths, and reveal how it’s laying the groundwork for a decentralized internet—Web 3.0.
What is Web 3.0?
In Web 2.0, data is stored and controlled by a few large corporations such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon. This creates privacy concerns and allows monopolization of personal information. Web 3.0 aims to change this by decentralizing control and empowering users with more control over their data and digital identity.
Web 3.0, or the ‘decentralized web,’ is the next phase of internet evolution, emphasizing user control and decentralization.
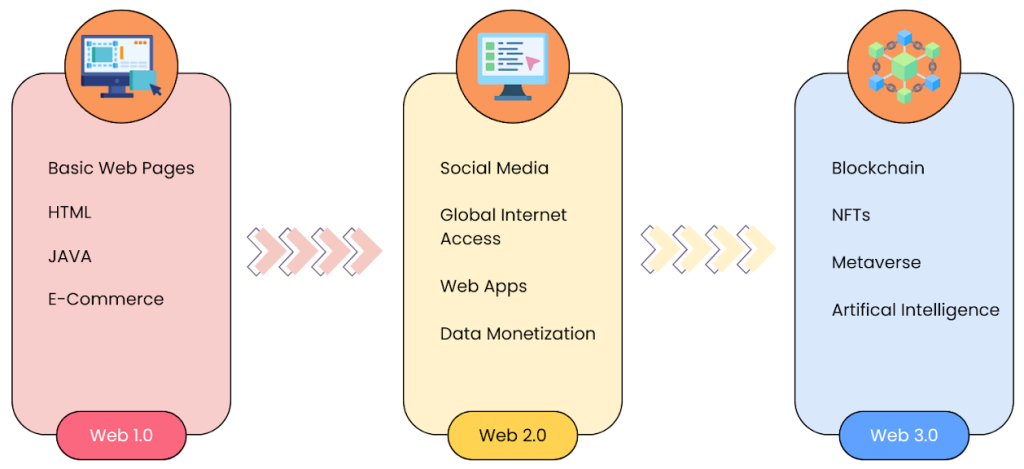
Figure 1: The Evolution of the Web – Web 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0
Key Principles of Web 3.0:
- Decentralization: Data on decentralized networks, not corporate servers.
- User Sovereignty: Users control their data.
- Native Payments: Direct digital payments without banks.
- Interoperability: Platforms connect seamlessly.
Blockchain is the backbone of Web 3.0, providing the decentralization needed to eliminate intermediaries and restore control to users.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows data to be stored globally across thousands of servers. The defining feature is that this data is immutable—meaning it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from network participants.
Imagine a ledger shared among thousands of computers (nodes) worldwide. Each new transaction is verified by these nodes and added to a “block.” When this block is full, it links to the previous one, forming a “chain.” This structure ensures that tampering with one block would alter all subsequent blocks, making it nearly impossible due to the decentralized verification process.
Key Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain.
- Transparency: Transactions are public and verifiable.
- Immutability: Data on the blockchain can’t be altered.
- Security: Strong cryptographic and decentralized consensus make blockchain secure.
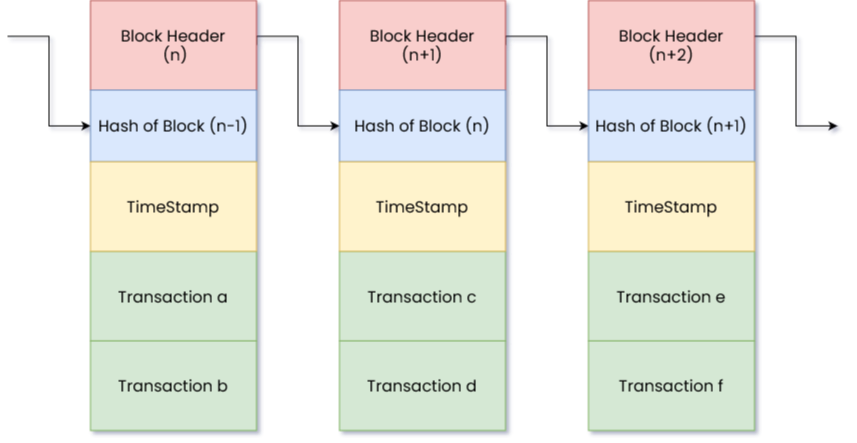
Figure 2: The Structure of a Blockchain – How Transactions Are Chained Together
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates via a network of nodes that verify each transaction. Transactions are grouped into blocks, and blocks are added to the chain after network consensus through mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Here’s a breakdown:
- Transaction Creation: One party sends information (like cryptocurrency or data) to another. This transaction is bundled with others into a “block.”
- Consensus Mechanism: To add a block to the chain, network nodes verify its validity. This is done via consensus mechanisms like:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, securing the network but requiring substantial energy.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are selected based on staked coins, making this approach faster and more energy-efficient.
- Adding to the Chain: Once validated, the block is added to the chain in a way that links it to previous blocks, forming an unchangeable chain. This structure ensures tampering with any block would require altering the entire chain, which is impractically difficult due to decentralized verification.
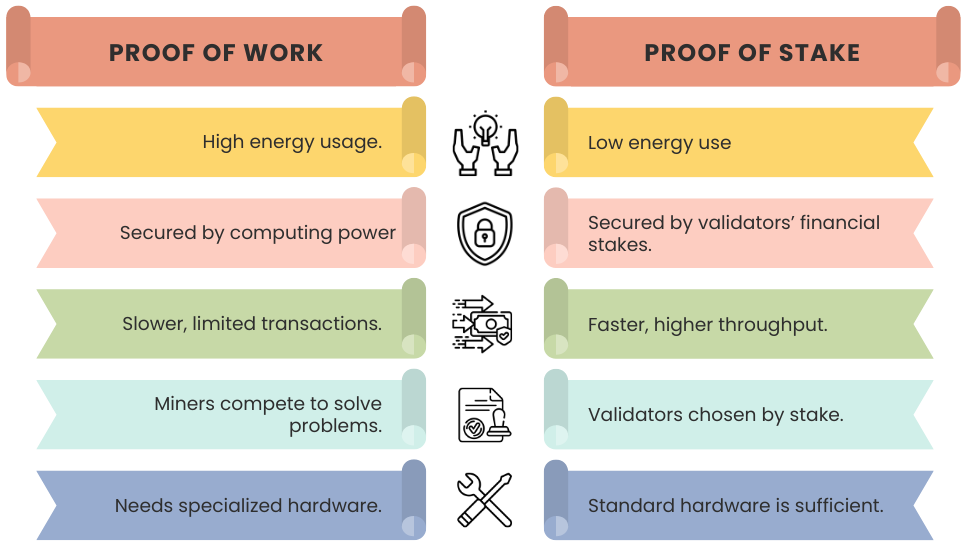
Figure 3: Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake – Key Differences
Blockchain use cases
Blockchain technology has transformed many sectors with endless applications.
1. Smart Contract
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that contain the terms of the code agreement and enforce those agreements through automated processes. It, thus, completely does away with the involvement of a third-party. For instance, when a verifiable mishap or an event occurs that is covered by an insurance policy, the insurer may automatically release the funds without delay to settle the claim. This innovation can streamline processes in the sectors such as real estate, insurance, finance, and legal services. For example, Tune.fm uses smart contracts to pay artists directly for music streaming, eliminating intermediaries.
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFT is a unique digital asset. It proves ownership of art, music, patent, copyright, and other virtual goods. Stored on a blockchain, it ensures safety, traceability, and authenticity. This makes it ideal for digital ownership of Intellectual property (IP) in gaming, collectibles, and event ticketing. For instance, consider “Everyday: The First 5000 Days,” a digital artwork by Beeple. It sold was as an NFT for $69 million at a Christie’s auction in March 2021. By 2021, the NFT game Axie Infinity generated $4.31 billion in all-time NFT sales. Players earned real money from in-game activities.
3. DAOs or (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations)
DAOs are a community-led entity. Code controls them completely, not management. There will be votes on proposals. This will ensure clear, democratic control over the resources and policies. This would be an ideal fit for investment funds, charitable groups, and communities with shared interests. For example Uniswap is a groundbreaking blockchain-powered exchange for blockchain-powered crypto-currency p2p trades, boasting a massive $8 billion market cap as of December 2024.
4. Tokenization of Assets
It is a transformation of real assets like art pieces, stocks, and property into digital tokens. This will enable fractional ownership and high-value assets priced much higher with increased liquidity and market coverage. For instance, in 2018, 18.9 percent of the resort hotel St. Regis Aspen was sold for $18 million in digital tokens.
5. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi refers to financial services, like lending and trading. They work without traditional banks. DeFi is giving users more independence in managing their finances. It transparently does this, without credit checks or intermediaries. For example Aave a leading DeFi has a TVL of over $15 Billion as of 19 December 2024.
Real-world applications of blockchain.
Blockchain technology is providing unmatched transparency, security, and efficiency in many sectors. Let’s examine some of the areas where blockchain creates a significant impact:
Finance: Ripple’s Cross-Border Payments
Ripple uses blockchain for near-instant and low-cost cross-border payments. Ripple’s unique consensus ledger and its digital asset (XRP) streamlines international transfers. They cut out intermediaries and fees. American Express uses Ripple to speed up traceable Cross-Border Payments transactions, thus increasing transparency and cost efficiency. Ripple allows users to settle international payments in a matter of seconds, while traditional transfers can take weeks or even months. Furthermore, it has reduced transaction fees by up to 60%. Over 300 financial institutions are now using Ripple’s for cross-border transactions.
Healthcare: Patient-centered data management on Medicalchain
Medicalchain is a blockchain based decentralized platform that enables secure, fast and transparent exchange and usage of medical data, giving patients the power to control who can access their medical records. This ensures accuracy, transparency, and privacy. Different stakeholders such as doctors, hospitals, laboratories, pharmacists, and health insurers can request permission to access a patient’s record – they will not own them. It helps reduce medical errors and enhances data security and patient privacy.
Supply Chain: IBM Food Trust for Food Safety
IBM’s Food Trust network provides better traceability for food on the move. Large retailers, like Walmart, use it to trace a product’s origin in seconds. This reduces contamination risks and offers full transparency. Each step from farms to shelves is stored to speed up recalls and authentications, hence combating fraud and saving on paper costs. Walmart reduced tracing the origin of food products from 7 days to 2.2 seconds. Improved traceability and recall processes from the platform have ensured that foodborne illness is on the decline.
Propy on Real Estate: Blockchain-Driven Transactions
Propy made real estate deals faster by recording property transactions without involving any third party. Blockchain locks down property records, removes any possibility of title tampering, and saves costs. Sellers can share the entire history of title transparently with their prospective buyers bringing about trust and convenience. Propy has facilitated real estate transactions of over $4 billion – all transparent and verifiable, decreasing disputes.
The Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers numerous advantages, which is why it has captured the attention of industries worldwide. Let’s break down the key benefits:
Security
Blockchain’s decentralized and encrypted nature makes it far more secure than traditional systems, which rely on centralized databases. The immutability of blockchain records ensures that data cannot be altered without widespread agreement.
Efficiency
Blockchain technology automates many processes and removes intermediaries, speeding up transactions and reducing costs. For instance, financial transactions that typically take days through banks can be completed in minutes with blockchain.
Transparency and Trust
Because all transactions on the blockchain are visible and verifiable by anyone in the network, it fosters a higher level of trust between participants. This is particularly valuable in industries where transparency is key, such as supply chain management and finance.
How Blockchain Achieves Security?
Security is one of blockchain’s most talked-about benefits. But how does it achieve such high levels of security?
Encryption
Blockchain uses cryptography to secure data. Each transaction is encrypted with both a public and a private key. The public key can be shared with anyone, while the private key is kept secret by the owner. This ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt and access the information.
Decentralization
Since blockchain data is distributed across a large network of nodes, there is no single point of failure. In traditional centralized systems, if a hacker gains access to the central database, they can wreak havoc. In a decentralized system, this is nearly impossible because the hacker would have to compromise a majority of nodes simultaneously.
Consensus Mechanisms
The use of consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake ensures that every transaction is validated by the network before being added to the blockchain. This decentralized validation process ensures that no single party can control the network or introduce fraudulent transactions.
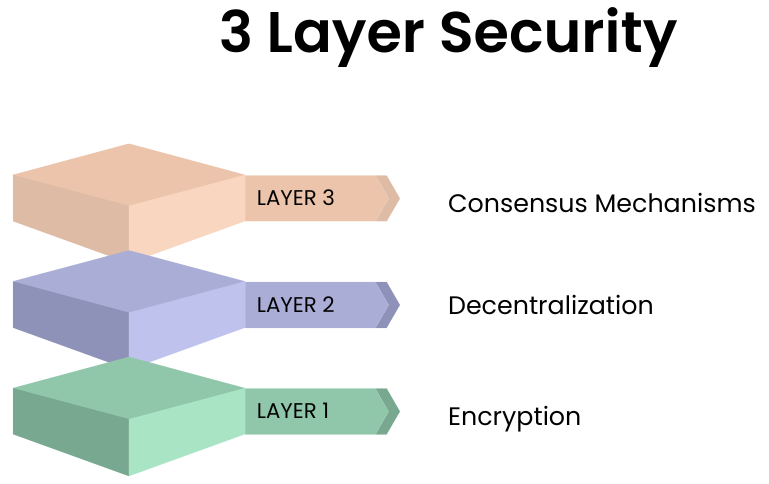
Figure 4: Blockchain’s Multiple Layers of Security
The Future of Blockchain: What Lies Ahead?
The future of blockchain is promising, and its applications are growing rapidly. As blockchain technology matures, we can expect to see more industries adopting decentralized systems to improve efficiency, transparency, and security. Web 3.0 is set to play a crucial role in shaping this future, with blockchain acting as its foundation.
However, there are still challenges to overcome, such as scalability, regulatory issues, and the energy consumption of certain consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work. Despite these hurdles, the momentum behind blockchain innovation is undeniable.
In summary, blockchain is revolutionizing how we think about data, security, and trust. Its decentralized nature makes it a perfect fit for a future where users regain control over their information, transactions are transparent, and the need for middlemen diminishes.
Myths About Blockchain
As with any new technology, blockchain has sparked some misconceptions. Let’s address the most common myths:
Q: Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
A: Blockchain is the underlying technology for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, but it serves many purposes beyond cryptocurrencies. It acts as a decentralized, secure ledger with applications in finance, healthcare, real estate, and supply chains, among other sectors.
Q: Is blockchain completely anonymous?
A: Blockchain transactions are pseudonymous, not anonymous. Public blockchains like Bitcoin show wallet addresses rather than personal identities. Private and consortium blockchains, however, may include identity verification, offering a mix of privacy and transparency.
Q: Is blockchain hack-proof?
A: While blockchain is highly secure due to decentralization and consensus protocols, it is not entirely immune to attacks. For instance, a 51% attack on a smaller blockchain could alter records, though this is costly and difficult to achieve on large networks.
Q: Does blockchain waste too much energy?
A: Some earlier blockchains, like Bitcoin, consumed substantial energy due to their Proof of Work (PoW) requirements. However, many newer blockchains use energy-efficient methods like Proof of Stake (PoS), and sustainable solutions are constantly emerging to reduce environmental impact.
Q: Is blockchain only useful for financial applications?
A: Blockchain has applications across a wide range of industries, including healthcare, supply chain, and real estate. For example, it secures patient data in healthcare and tracks product origins in supply chains, demonstrating its value beyond finance.
Q: Are all blockchains public and decentralized?
A: Blockchains can be public, private, or consortium-based. Public blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin) allow anyone to participate, while private ones limit access, making them suitable for enterprises that require controlled environments.
Q: Is blockchain all hype with no real-world uses?
A: Blockchain has demonstrated real-world value in applications like IBM’s Food Trust for food safety and Ripple’s cross-border payments. Its adoption is expanding as industries recognize blockchain’s benefits for transparency and efficiency.
Conclusion
Blockchain’s decentralized, secure nature is transforming industries, from finance and healthcare to supply chains. By enabling peer-to-peer transactions, enhancing data security, and removing intermediaries, blockchain is paving the way for a more efficient, decentralized future.
What could blockchain mean for your industry? From enhancing transparency to creating new efficiencies, its potential is just beginning to unfold we’re here to help you stay ahead. DataCouch offers a range of expert-led courses that will build your blockchain knowledge from the ground up. Start with Introduction to Web 3.0, where you’ll learn about the next generation of the internet and its foundation in blockchain.
From there, dive into Hyperledger Fabric for enterprise blockchain solutions or explore Ethereum Development for building decentralized applications. These courses will equip you with the skills to leverage blockchain technology and thrive in this rapidly evolving ecosystem.

